Machine Learning Tutorial 01 - Regression (1)
I 지도 학습 VS 비지도 학습
머신러닝은 크게 두 가지 유형으로 분류한다. 우선 아래 표를 보자.
| 구분 | 지도학습(Supervised Learning) | 비지도 학습(Unsupervised Learning) |
|---|---|---|
| 알고리즘(분석모형) | 회귀분석분류모형 | 군집분석 |
| 특징 | 정답을 알고 있는 상태에서 학습모형 평가 방법이 다양한 편 | 정답이 없는 상태에서 서로 비슷한 데이터를 찾아서 그룹화모형 평가 방법이 제한적 |
지도학습(Supervised Learning)은 종속변수(Dependent Variable) 선정이 매우 중요하며. 종속변수 선정과 함께 데이터 분석도 같이 병행이 된다. 그러나 비지도학습(Unsupervised Learning)은 데이터가 많은데, 어떻게 분류하면 좋을지 모를 때 서로 비슷한 특징끼리 결합 및 그룹화 하는 것을 말한다.
II. 회귀모형 예제
우선 회귀모형 모형부터 만들자. 아래 코드를 그대로 실행하면 될 것이다. 만약 파이썬(Python) 설치가 필요한 사람은 Tensorflow 2.0 Installation에서 설치 방법을 따라 설치를 진행하기를 바란다.
## 기본 라이브러리 불러오기
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn import metrics
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ModuleNotFoundError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-1-5e3e002ab9bf> in <module>
2 import pandas as pd
3 import numpy as np
----> 4 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5 import seaborn as sns
6 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'matplotlib'
(1) No Module Names ’name_of_library'
가끔 이런 모듈이 없다고 나올 때가 있다. 이해하기 어려운 것은 아니다. 가장 좋은 것은 언제나 에러 메시지 전체를 복사해서 구글에서 검색을 한 뒤 해결책을 빠르게 찾는 것이 좋다.
위 에러는 matplotlib 모듈이 없다는 뜻이다.
그럼 설치를 해보자. 어떻게? 자세한 내용은 공식문서를 참고한다. matplotlib 간단한 설치방법은 아래와 같다.
터미널에서 아래와 같이 입력한다. 참고로 MacOS / 필자는 pip3로 설치할 예정이다. 윈도우 아나콘다 설치 버전
$ python3 -m pip install -U pip
$ python3 -m pip install -U matplotlib
matplotlib와 마찬가지로 seaborn 그리고 scikit-learn 모듈도 같이 위와 같은 형태로 설치를 하면 된다.
(2) Sample Tutorial
전체 소스코드를 실행한 뒤, 하나씩 간단하게 설명을 진행하도록 한다.
import io
import requests
import pprint
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chloevan/datasets/master/weather/Weather.csv"
url = requests.get(url).content
weather_df = pd.read_csv(io.StringIO(url.decode('utf-8')))
pprint.pprint(weather_df.head())
STA Date Precip WindGustSpd MaxTemp MinTemp MeanTemp \
0 10001 1942-7-1 1.016 NaN 25.555556 22.222222 23.888889
1 10001 1942-7-2 0 NaN 28.888889 21.666667 25.555556
2 10001 1942-7-3 2.54 NaN 26.111111 22.222222 24.444444
3 10001 1942-7-4 2.54 NaN 26.666667 22.222222 24.444444
4 10001 1942-7-5 0 NaN 26.666667 21.666667 24.444444
Snowfall PoorWeather YR ... FB FTI ITH PGT TSHDSBRSGF SD3 RHX RHN \
0 0 NaN 42 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
1 0 NaN 42 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2 0 NaN 42 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
3 0 NaN 42 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
4 0 NaN 42 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
RVG WTE
0 NaN NaN
1 NaN NaN
2 NaN NaN
3 NaN NaN
4 NaN NaN
[5 rows x 31 columns]
pprint.pprint(weather_df.describe())
STA WindGustSpd MaxTemp MinTemp \
count 119040.000000 532.000000 119040.000000 119040.000000
mean 29659.435795 37.774534 27.045111 17.789511
std 20953.209402 10.297808 8.717817 8.334572
min 10001.000000 18.520000 -33.333333 -38.333333
25% 11801.000000 29.632000 25.555556 15.000000
50% 22508.000000 37.040000 29.444444 21.111111
75% 33501.000000 43.059000 31.666667 23.333333
max 82506.000000 75.932000 50.000000 34.444444
MeanTemp YR MO DA DR \
count 119040.000000 119040.000000 119040.000000 119040.000000 533.000000
mean 22.411631 43.805284 6.726016 15.797530 26.998124
std 8.297982 1.136718 3.425561 8.794541 15.221732
min -35.555556 40.000000 1.000000 1.000000 2.000000
25% 20.555556 43.000000 4.000000 8.000000 11.000000
50% 25.555556 44.000000 7.000000 16.000000 32.000000
75% 27.222222 45.000000 10.000000 23.000000 34.000000
max 40.000000 45.000000 12.000000 31.000000 78.000000
SPD ... FT FB FTI ITH PGT SD3 RHX RHN RVG \
count 532.000000 ... 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 525.000000 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
mean 20.396617 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 12.085333 NaN NaN NaN NaN
std 5.560371 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 5.731328 NaN NaN NaN NaN
min 10.000000 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 0.000000 NaN NaN NaN NaN
25% 16.000000 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 8.500000 NaN NaN NaN NaN
50% 20.000000 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 11.600000 NaN NaN NaN NaN
75% 23.250000 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 15.000000 NaN NaN NaN NaN
max 41.000000 ... NaN NaN NaN NaN 23.900000 NaN NaN NaN NaN
WTE
count 0.0
mean NaN
std NaN
min NaN
25% NaN
50% NaN
75% NaN
max NaN
[8 rows x 24 columns]
X = weather_df['MinTemp'].values.reshape(-1,1)
y = weather_df['MaxTemp'].values.reshape(-1,1)
# 데이터 셋 분리
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# 모형 개발 선언
regressor = LinearRegression()
regressor.fit(X_train, y_train) # 알고리즘 트레이닝
# intercept: 상수
pprint.pprint(regressor.intercept_)
# slope: 기울기
pprint.pprint(regressor.coef_)
# 예측
y_pred = regressor.predict(X_test)
# 데이터 셋 비교
pred_df = pd.DataFrame({'실제값': y_test.flatten(), '예측값': y_pred.flatten()})
pprint.pprint(pred_df.head())
array([10.66185201])
array([[0.92033997]])
실제값 예측값
0 28.888889 33.670351
1 31.111111 30.091251
2 27.222222 26.512151
3 28.888889 31.113851
4 23.333333 15.774852
# 테스트 데이터와 예측값의 기울기 비교
plt.scatter(X_test, y_test, color='gray')
plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color='red', linewidth=2)
plt.show()
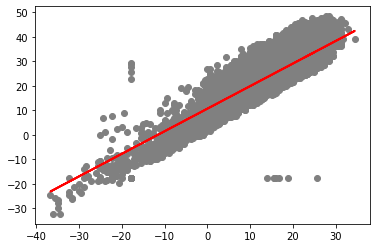
# 모형 성능
print('MAE:', metrics.mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred))
print('MSE:', metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print('RMSE:', np.sqrt(metrics.mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)))
MAE: 3.19932917837853
MSE: 17.631568097568447
RMSE: 4.198996082109204
위 소스코드의 구체적인 설명자료는 Machine Learning Tutorial 02 - Regression (2)를 참고하시기를 바랍니다.
III. Reference
Chauhan, N. S. (2019, September 7). A beginner’s guide to Linear Regression in Python with Scikit-Learn. Retrieved March 19, 2020, from https://towardsdatascience.com/a-beginners-guide-to-linear-regression-in-python-with-scikit-learn-83a8f7ae2b4f
End of Document
