Python Sales Dashboard Using Dash and Plotly
Page content
개요
- Sales 데이터를 활용하여 대시보드를 만드는 과정을 제작한다.
- 기본 파이썬 코딩은 할 줄 안다는 전제하에 작성하며, 세부 내용이 필요하면 참고 자료를 확인할 것을 권한다.
- 윈도우 10에서 본 프로젝트를 수행하였다.
Chapter 1. Github Repo 생성
- 필자는 Github 레포를 만들었다. (Repo 명: python_dash_sales)
- git clone을 통해서 로컬로 가져온다.
$ git clone https://github.com/your_id/python_dash_sales.git
Chapter 2. Python 프로젝트 생성
-
PyCharm을 주 에디터로 사용할 예정이다.
- 파이썬은 아나콘다로 설치하였고, 이 때 환경변수 설정은 잘 되어 있는지 확인한다.
- 필자는 3.8.8이 기본 버전임을 확인했다.
$ python --version Python 3.8.8 -
git clone한 폴더에서 바로 PyCharm 프로젝트로 열 수 있다.
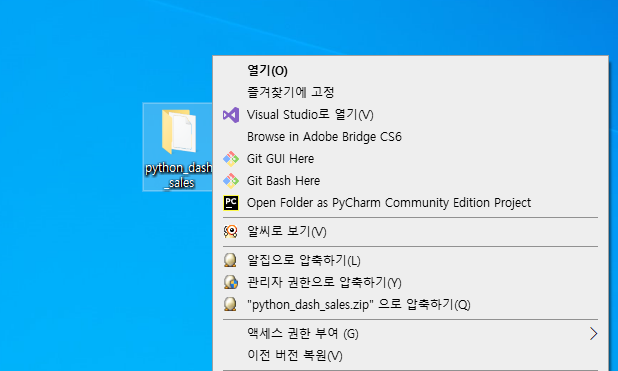
- 파일을 열면 아래와 같은 화면으로 이동한다.
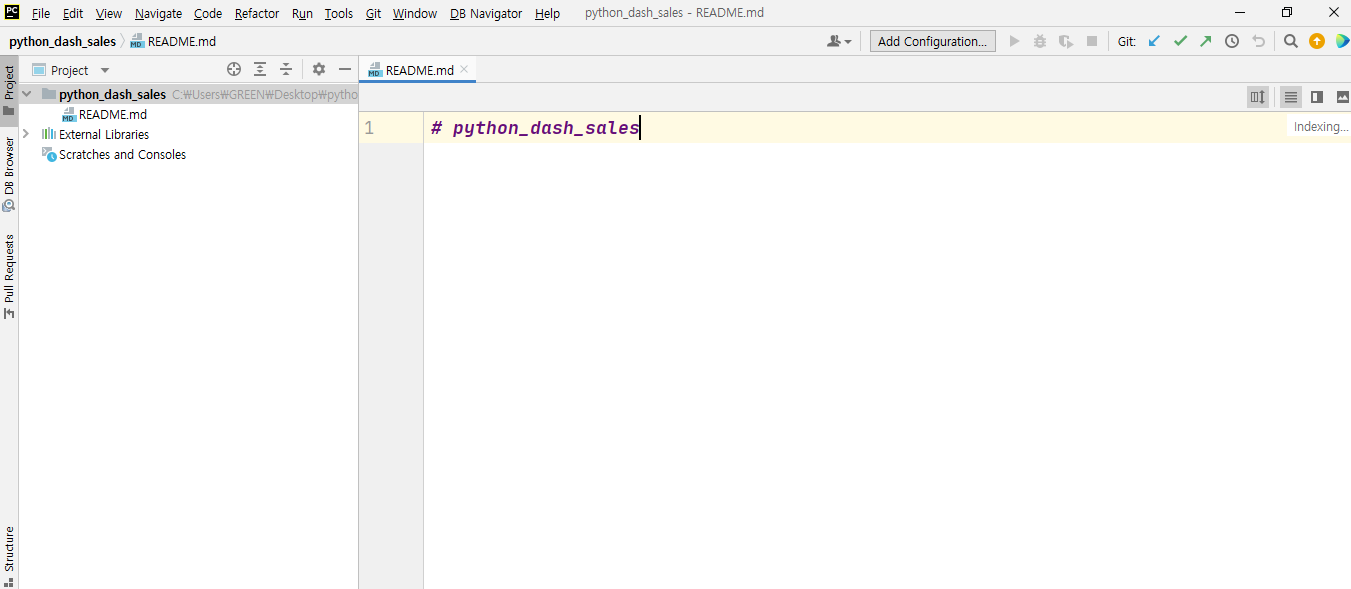
- 여기에서 가상 환경을 쉽게 설정 할 수 있다.
- 가상환경은 가급적 virtualenv로 하는 것을 추천한다 (특별한 이유는 없다).
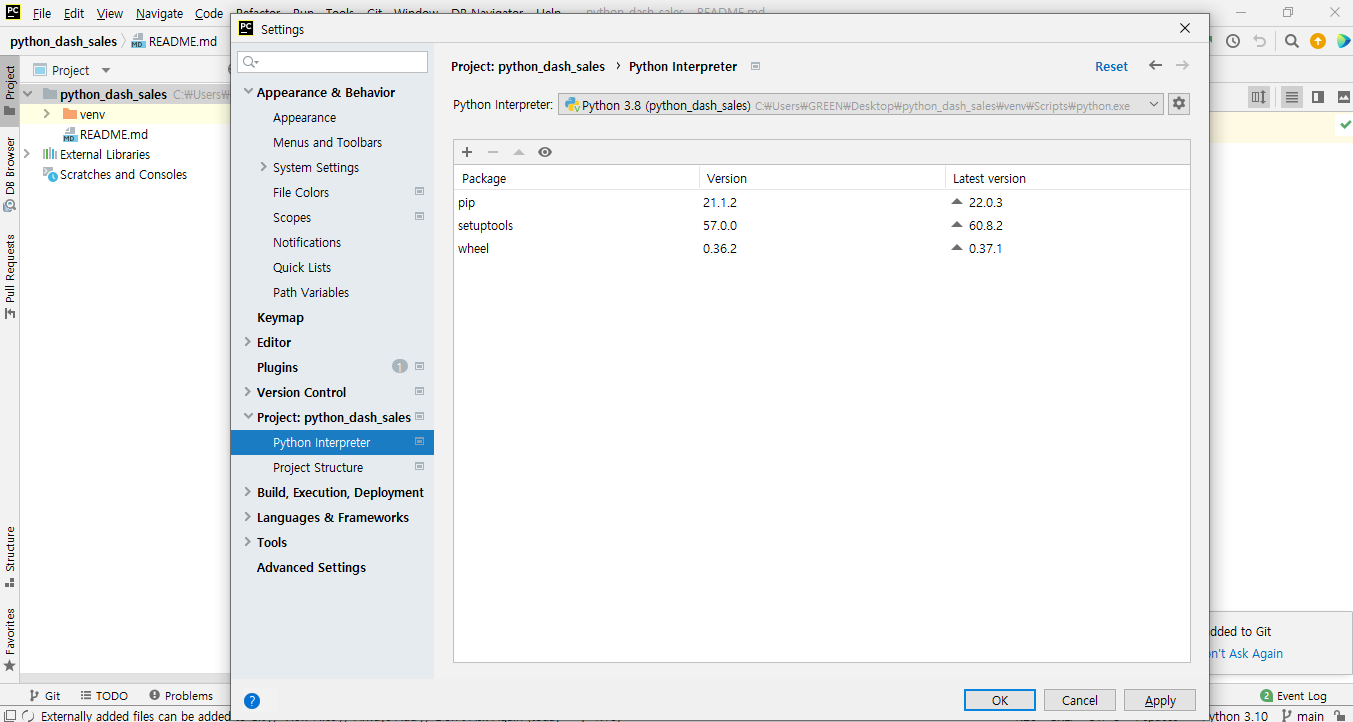
- [File] - [Settings] - [Project] - [Python Interpreter] - [설정: 바퀴모양] - [Add]을 순차적으로 클릭한다.
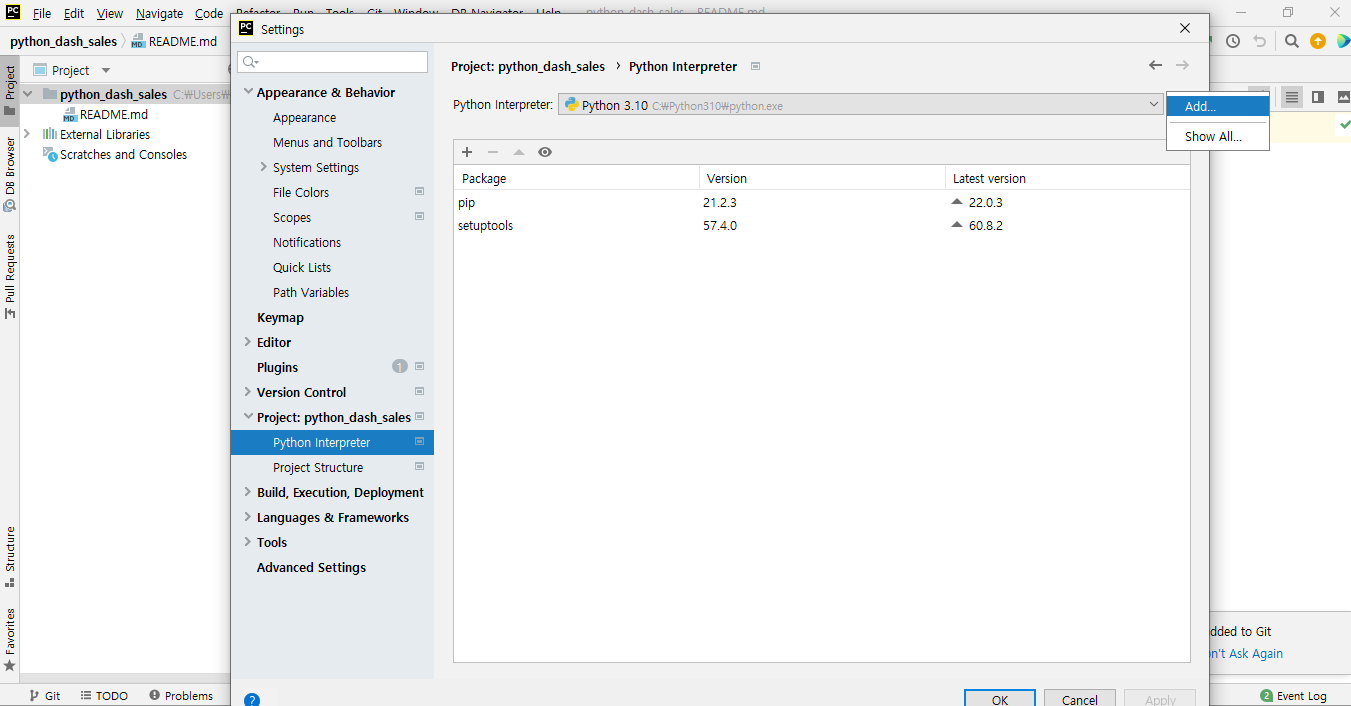
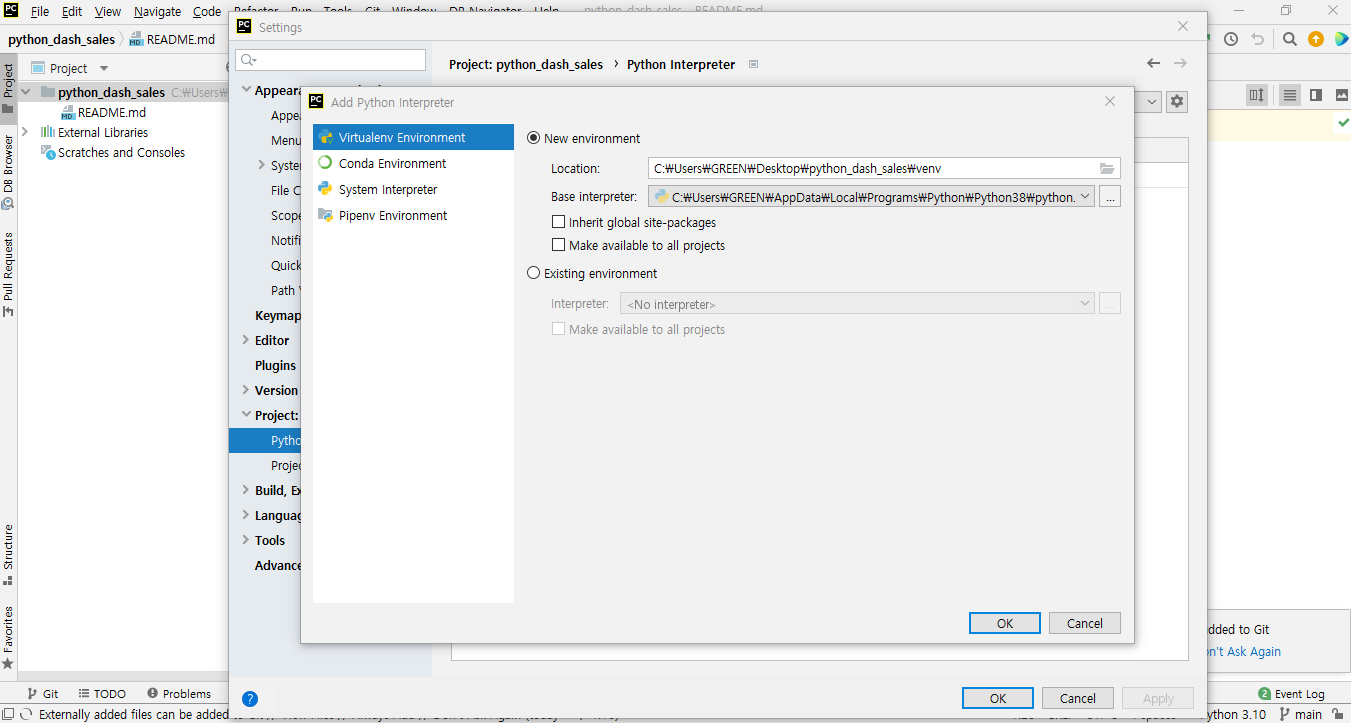
- 아래 화면에서
OK버튼을 클릭하면 된다.
- 설치가 완료가 되면,
venv폴더가 생성이 된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- 설치가 완료가 된 다음에는 터미널에서
which python을 실행하여 python이 어디에서 실행되는지 확인한다.
$ which python
/c/Users/your_name/Desktop/python_dash_sales/venv/Scripts/python
Chapter 3. 라이브러리 설치
- 라이브러리 설치를 위해서는
requirements.txt파일을 하나 만들고, 아래 라이브러리를 복사하여 붙여 넣는다. (Project ROOT경로에 위치)
ansi2html==1.6.0
anyio==2.2.0
appnope==0.1.2
argon2-cffi==20.1.0
async-generator==1.10
attrs==20.3.0
Babel==2.9.0
backcall==0.2.0
bleach==3.3.0
Brotli==1.0.9
certifi==2020.12.5
cffi==1.14.5
chardet==4.0.0
click==7.1.2
dash==1.19.0
dash-bootstrap-components==0.11.3
dash-core-components==1.15.0
dash-html-components==1.1.2
dash-renderer==1.9.0
dash-table==4.11.2
decorator==4.4.2
defusedxml==0.7.1
entrypoints==0.3
Flask==1.1.2
Flask-Compress==1.9.0
future==0.18.2
gunicorn==20.0.4
idna==2.10
ipykernel==5.5.0
ipython==7.21.0
ipython-genutils==0.2.0
itsdangerous==1.1.0
jedi==0.18.0
Jinja2==2.11.3
joblib==1.0.1
json5==0.9.5
jsonschema==3.2.0
jupyter-client==6.1.12
jupyter-core==4.7.1
jupyter-dash==0.4.0
jupyter-packaging==0.7.12
jupyter-server==1.4.1
jupyterlab==3.0.12
jupyterlab-pygments==0.1.2
jupyterlab-server==2.3.0
MarkupSafe==1.1.1
mistune==0.8.4
nbclassic==0.2.6
nbclient==0.5.3
nbconvert==6.0.7
nbformat==5.1.2
nest-asyncio==1.5.1
notebook==6.2.0
numpy==1.20.1
packaging==20.9
pandas==1.2.3
pandocfilters==1.4.3
parso==0.8.1
pexpect==4.8.0
pickleshare==0.7.5
plotly==4.14.3
prometheus-client==0.9.0
prompt-toolkit==3.0.17
ptyprocess==0.7.0
pycparser==2.20
Pygments==2.8.1
pyparsing==2.4.7
pyrsistent==0.17.3
python-dateutil==2.8.1
pytz==2021.1
pyzmq==22.0.3
requests==2.25.1
retrying==1.3.3
scikit-learn==0.24.1
scipy==1.6.1
Send2Trash==1.5.0
six==1.15.0
sklearn==0.0
sniffio==1.2.0
terminado==0.9.3
testpath==0.4.4
threadpoolctl==2.1.0
tornado==6.1
traitlets==5.0.5
urllib3==1.26.4
wcwidth==0.2.5
webencodings==0.5.1
Werkzeug==1.0.1
xlrd>=1.0.0
- 해당 라이브러리들을 설치한다.
$ pip install -r requirements.txt
- 아래와 같이 정상적으로 설치가 되면 끝이다.
- 그 외
s1.css와style.css별도로 작성한다. (assets 폴더 아래 위치)- s1.css : https://codepen.io/chriddyp/pen/bWLwgP.css
- style.css
body {
background-color: #192444;
margin: 5%;
}
#title1 {
text-align: center;
}
#title2 {
text-align: center;
}
#title3 {
text-align: center;
}
.create_container2 {
align-items: center;
border-radius: 15px;
background-color: #1f2c56;
margin: 10px;
padding: 15px;
position: relative;
box-shadow: 2px 2px 2px 2px #1f2c56;
}
.dcc_compon {
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 5px;
width: calc(100%-40px);
}
.fix_label {
font-size: 20px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 10px;
padding-bottom: 0px;
margin-bottom: 0px;
width: calc(100%-40px);
}
.container-display {
display: flex;
}
#header {
align-items: center;
}
.flex-display {
display: flex;
}
#mainContainer {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.rc-slider-track {
background-color: red;
}
.rc-slider-dot-active {
border-color: red;
border: solid 2px red;
}
.rc-slider-handle {
background-color: red;
border-color: red;
}
.rc.slider-handle:hover {
border-color: red;
}
.rc.slider-handle-active:active {
border-color: red;
}
/* width */
::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 10px !important;
display: block !important;
}
/* Track */
::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
background: #1f2c56 !important;
border-radius: 10px !important;
display: block !important;
}
/* Handle */
::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
background: #192444;
}
/* Handle on hover */
::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb:hover {
background: white !important;
}
- train.csv 파일은 아래 링크에서 다운로드 받는다.
- 링크:
Chapter 4. Dash 코드 작성
- 순차적으로 코드를 작성하도록 한다.
- 완성하려고 하는 대시보드는 다음과 같다.
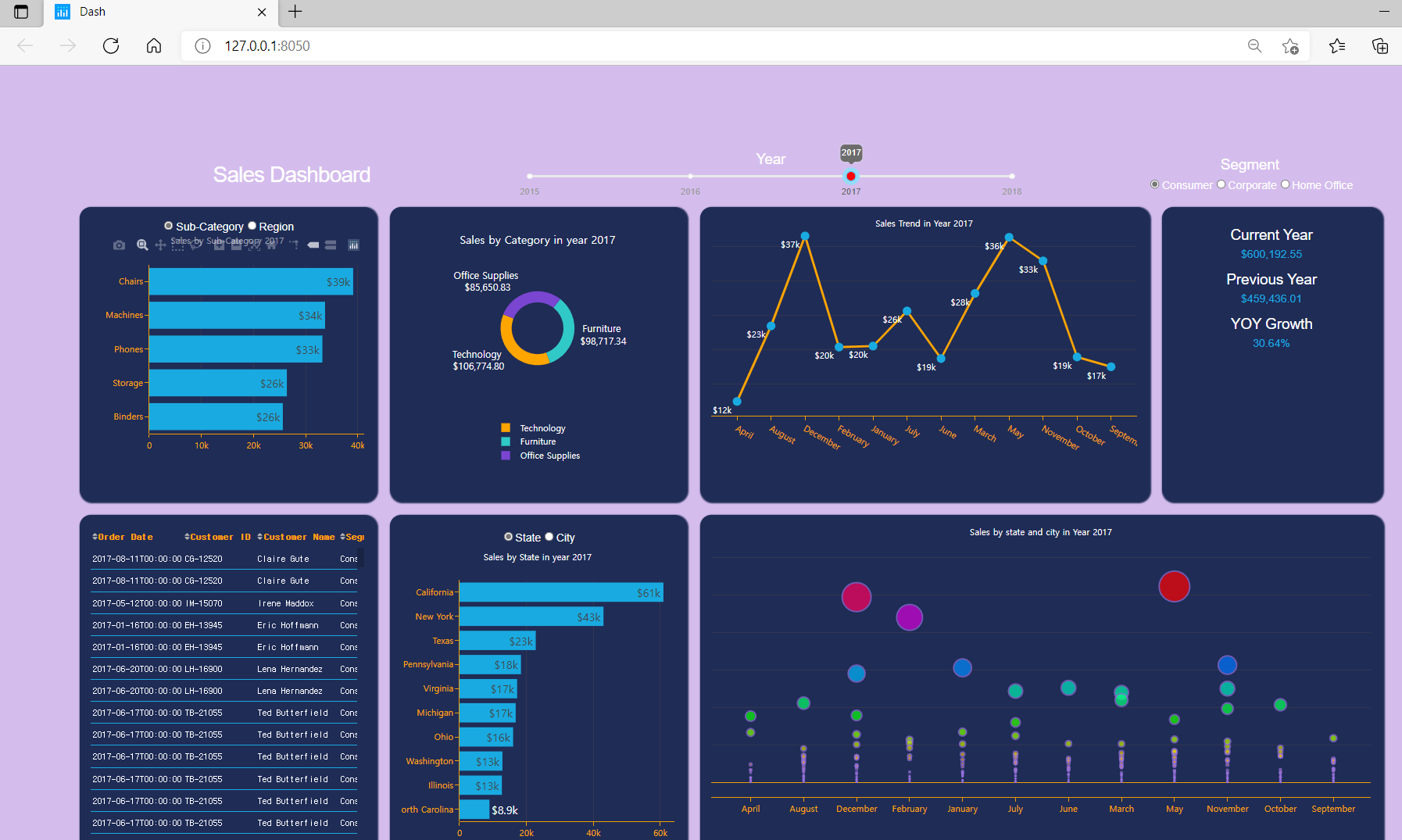
(1) Dash App Title
- Title을 추가한 후, 대시보드를 작성한다.
- meta_tags를 추가하면, 모바일 등에도 반응형(interactive) 형태로 화면이 동적으로 바뀐다.
import dash
import dash_html_components as html
import dash_core_components as dcc
from dash.dependencies import Input, Output
import plotly.graph_objects as go
import pandas as pd
sales = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
app = dash.Dash(__name__, meta_tags=[{"name" : "viewport",
"content" : "width=device-width"}])
app.layout = html.Div([
html.Div([
html.Div([
html.H3("Sales Dashboard",
style = {"margin-bottom" : '0px',
"color" : "white"})
], className="one third column", id = "title1")
], id = "header",
className="row flex-display",
style = {"margin-bottom" : '0px',
"color" : "white"})
], id = "mainContainer", style={'display' : "flex", "flex-direction" : "column"})
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run_server(debug=True)
- 아래와 같이 실행한다.
$ python index.py
Dash is running on http://127.0.0.1:8050/
* Serving Flask app "index" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: on
(2) Slider 기능 추가
- Slider 기능을 추가하는 코드를 작성한다.
- 코드는
id = titlle1다음에 작성한다. - Slider 참고 자료: https://dash.plotly.com/dash-core-components/slider
- 코드는
app.layout = html.Div([
...
], className="one third column", id = "title1"),
# slider (2)
html.Div([
html.P('Year', className='fix_label', style = {'color' : 'white'}),
dcc.Slider( id = 'select_years',
included=False,
updatemode='drag',
tooltip= {'always_visible': True},
min = 2015,
max = 2018,
step = 1,
value = 2018,
marks = {str(yr): str(yr) for yr in range(2015, 2018)},
className="dcc-compon"), # slider (2)
], className="one-half column", id = 'title2')
], ...
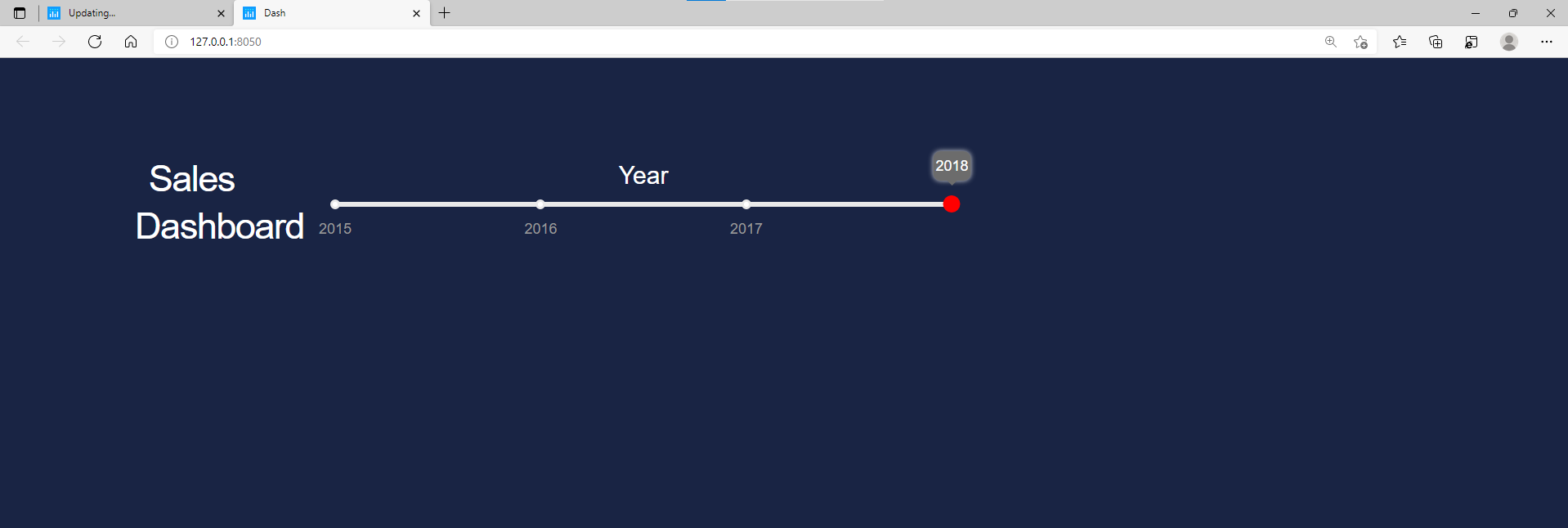
(3) Radio 버튼 추가
- Radio 버튼 기능을 추가하는 코드를 작성한다.
- 코드는
Slider코드 다음에 이어서 작성한다. - RadioItems 참고 자료: https://dash.plotly.com/dash-core-components/radioitems
- 코드는
app.layout = html.Div([
...
], className="one-half column", id = 'title2'), # slider (2)
# Radio (3) # 작업할 것
html.Div([
html.P('Segment', className='fix_label', style={'color': 'white'}),
dcc.RadioItems(id='radio_items',
labelStyle = {'display' : 'inline-block'},
value='Consumer',
options = [{'label': i, 'value' : i} for i in sales['Segment'].unique()],
style={'text-align' : 'center', 'color': 'white'},
className="dcc-compon"),
], className="one-third column", id='title3') # Radio (3) # 작업할 것
], ...
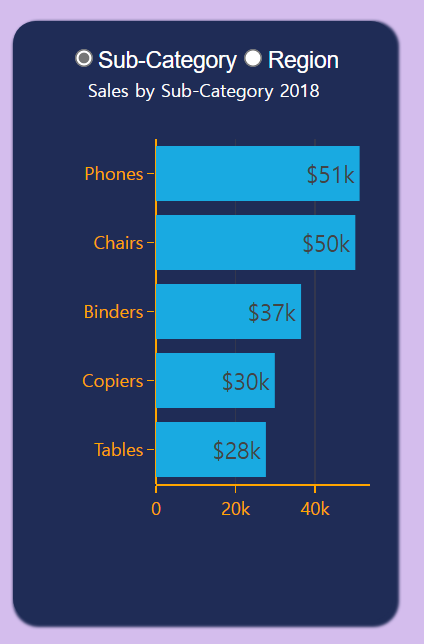
(4) 가로형 막대 그래프 추가
- 지금까지 배운 것을 토대로 다음과 같은 그래프를 추가할 것이다.
- 해당 그래프를 만들기 위해서는 크개 두개의
Component가 필요하다.
app.layout = html.Div([
...
], className="one-third column", id='title3') # Radio (3) # 작업할 것
], id = "header", className="row flex-display", style = {"margin-bottom" : '0px', "color" : "white"}),
html.Div([
# (4) 가로형 막대 그래프
html.Div([
dcc.RadioItems(id='radio_items1',
labelStyle={'display': 'inline-block'},
value='Sub-Category',
options=[{'label': 'Sub-Category', 'value': 'Sub-Category'},
{'label': 'Region', 'value' : 'Region'}],
style={'text-align': 'center', 'color': 'white'},
className="dcc-compon"),
dcc.Graph(id = 'bar_chart_1', config={'displayModeBar' : 'hover'}, style={'height': '350px'})
], className='create_container2 three columns', style={'height' : '400px'})
], className='row flex-display')
], id = "mainContainer", style={'display' : "flex", "flex-direction" : "column"}) # app.layout = html.Div
- 그다음 중요한 것이 Callback 사용이다.
- Callback에 관한 기본 튜토리얼은 다음 링크를 참조한다.
- 참조: https://dash.plotly.com/basic-callbacks
- 그래프 작성 시, 고려할 사항은 크게 두가지다.
- 독립변수에 해당하는 컬럼은 크게 Sub-Category & Region으로 구분된다.
- 해당 구문은 조건문으로 작성을 하도록 한다.
- 먼저, Year, Column이 존재하지 않기 때문에, 해당 코드를 생성하는 코드를 작성한다.
...
sales = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
sales['Order Date'] = pd.to_datetime(sales['Order Date'])
sales['Year'] = sales['Order Date'].dt.year
sales['Month'] = sales['Order Date'].dt.month_name()
...
- 다음은 Callback 영역을 작성하는 코드이다. 코드에 관한 구체적인 설명은 생략한다.
# 그래프 작성 구간 (Callback), # (4) 가로형 막대 그래프
@app.callback(Output('bar_chart_1', 'figure'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items1', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years, radio_items, radio_items1):
sales1 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'Sub-Category', 'Segment'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales2 = sales1[(sales1['Year'] == select_years) & (sales1['Segment'] == radio_items)].\
sort_values(by = ['Sales'], ascending=True).nlargest(5, columns = ['Sales'])
sales3 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'Region', 'Segment'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales4 = sales3[(sales3['Year'] == select_years) & (sales3['Segment'] == radio_items)].sort_values(by=['Sales'],ascending=False)
if radio_items1 == 'Sub-Category':
return {
'data': [
go.Bar(
x = sales2['Sales'],
y = sales2['Sub-Category'],
text = sales2['Sales'],
texttemplate ='$' + '%{text:,.2s}',
textposition ='auto',
orientation ='h',
marker=dict(color='#19AAE1'),
hoverinfo='text',
hovertext=
'<b>Year</b>: ' + sales2['Year'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Segment</b>: ' + sales2['Segment'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sub-Category</b>: ' + sales2['Sub-Category'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sales</b>: $' + [f'{x:,.0f}' for x in sales2['Sales']] + '<br>'
),
], # data
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales by Sub-Category' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.99,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 12},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=15),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#010915',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7},
margin=dict(t=40, r=0),
xaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12) # tickfont
), # xaxis
yaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
autorange='reversed',
showline=False,
showgrid=False,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12) # tickfond
) # yaxis
) # Layout
} # return if
elif radio_items1 == 'Region':
return {
'data': [
go.Bar(
x = sales4['Sales'],
y = sales4['Region'],
text = sales4['Sales'],
texttemplate ='$' + '%{text:,.2s}',
textposition ='auto',
orientation ='h',
marker=dict(color='#19AAE1'),
hoverinfo='text',
hovertext=
'<b>Year</b>: ' + sales4['Year'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Segment</b>: ' + sales4['Segment'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Region</b>: ' + sales4['Region'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sales</b>: $' + [f'{x:,.0f}' for x in sales4['Sales']] + '<br>'
),
], # data
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales by Region' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.99,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 12},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=15),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#010915',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7},
margin=dict(t=40, r=0),
xaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12) # tickfont
), # xaxis
yaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
autorange='reversed',
showline=False,
showgrid=False,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12) # tickfond
) # yaxis
) # Layout
} # return elif
- Layout에 관한 다양한 Parameters에 관한 설명은 다음 링크에서 참조한다.
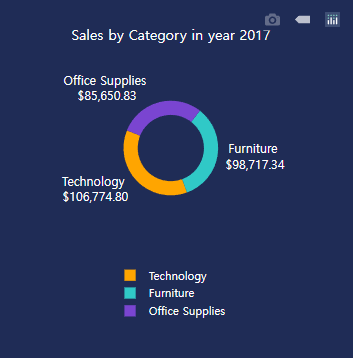
(5) 도넛 그래프 추가
- 도넛 차트를 그리기 위해 우선 기본 골격을 만들도록 한다.
...
], className='create_container2 three columns', style={'height' : '400px'}), # (4) 가로형 막대 그래프
# (5) 도넛 차트
html.Div([
dcc.Graph(id='donut_chart', config={'displayModeBar': 'hover'},
style={'height': '350px'})
], className='create_container2 three columns', style={'height': '400px'}), # (5) 도넛 차트
], className='row flex-display')
], id = "mainContainer", style={'display' : "flex", "flex-direction" : "column"}) # app.layout = html.Div
- 기존 그래프와 마찬가지로 callback 함수를 작성한다.
...
# 그래프 작성 구간 (Callback), # (5) 도넛 차트
@app.callback(Output('donut_chart', 'figure'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years, radio_items):
sales5 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'Category', 'Segment'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales_furniture = \
sales5[(sales5['Year'] == select_years) & (sales5['Segment'] == radio_items) & (sales5['Category'] == 'Furniture')][
'Sales'].sum()
sales_Office = sales5[(sales5['Year'] == select_years) & (sales5['Segment'] == radio_items) & (
sales5['Category'] == 'Office Supplies')]['Sales'].sum()
sales_Technology = sales5[
(sales5['Year'] == select_years) & (sales5['Segment'] == radio_items) & (sales5['Category'] == 'Technology')][
'Sales'].sum()
colors = ['#30C9C7', '#7A45D1', 'orange']
return {
'data': [go.Pie(
labels=['Furniture', 'Office Supplies', 'Technology'],
values=[sales_furniture, sales_Office, sales_Technology],
marker=dict(colors=colors),
hoverinfo='label+value+percent',
textinfo='label+value',
texttemplate='%{label} <br>$%{value:,.2f}',
textposition='auto',
textfont=dict(size=13),
hole=.7,
rotation=160,
# insidetextorientation= 'radial'
)],
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales by Category in year' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.93,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 15},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=12),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#1f2c56',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7}
)
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run_server(debug=True)
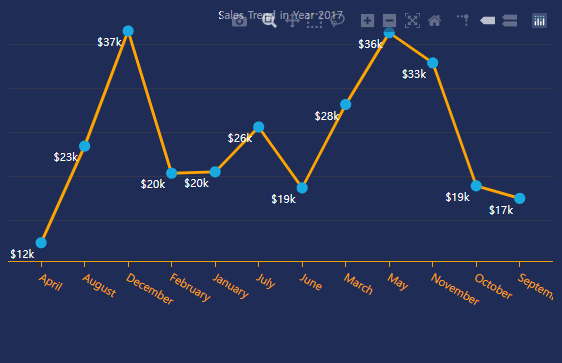
(6) 선 그래프 추가
- 선 그래프를 추가하는 코드를 작성하기 위한 기본 골격을 작성한다.
...
], className='create_container2 three columns', style={'height': '400px'}), # (5) 도넛 차트
# (6) 라인 그래프
html.Div([
dcc.Graph(id='line_chart', config={'displayModeBar': 'hover'},
style={'height': '350px'})
], className='create_container2 four columns', style={'height': '400px'}), # (6) 라인 그래프
- 기존 그래프와 마찬가지로 callback 함수를 작성한다.
...
# 그래프 작성 구간 (Callback), # (6) 라인 그래프
@app.callback(Output('line_chart', 'figure'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years, radio_items):
sales6 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'Month', 'Segment'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales7 = sales6[(sales6['Year'] == select_years) & (sales6['Segment'] == radio_items)]
return {
'data': [
go.Scatter(
x=sales7['Month'],
y=sales7['Sales'],
text=sales7['Sales'],
texttemplate='$' + '%{text:,.2s}',
textposition='bottom left',
mode='markers+lines+text',
line=dict(width=3, color='orange'),
marker=dict(color='#19AAE1', size=10, symbol='circle',
line=dict(color='#19AAE1', width=2)),
hoverinfo='text',
hovertext=
'<b>Year</b>: ' + sales7['Year'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Month</b>: ' + sales7['Month'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Segment</b>: ' + sales7['Segment'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sales</b>: $' + [f'{x:,.0f}' for x in sales7['Sales']] + '<br>'
),
],
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales Trend in Year' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.99,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 12},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=12),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#010915',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7},
margin=dict(t=5, l=0, r=0),
xaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=True,
showgrid=False,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)),
yaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=False,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=False,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)
)
)
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run_server(debug=True)
(7) 텍스트 추가
- KPI를 작성하는 Layout을 추가한다.
- Dive 태그 안에, 텍스트가 업데이트 될 Div가 추가가 된 것을 기억한다.
...
], className='create_container2 four columns', style={'height': '400px'}), # (6) 라인 그래프
# (7) 연도별 주요 지표
html.Div([
html.Div(id='text1'),
html.Div(id='text2'),
html.Div(id='text3'),
], className='create_container2 two columns'), # 연도별 주요 지표
], className='row flex-display'), # 상위 Div
...
- 이번에는 Callback 구문을 작성한다. 여기에서 주목해야 하는 것은
html.P관련 코드이다. Pandas 라이브러리를 통해 집계한 값을 각각html.P값에 추가하였다.
...
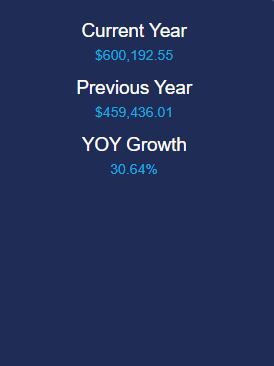
# (7) KPI 주요 지표
@app.callback(Output('text1', 'children'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years):
sales8 = sales.groupby(['Year'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
current_year = sales8[(sales8['Year'] == select_years)]['Sales'].sum()
return [
html.H6(children='Current Year',
style={'textAlign': 'center',
'color': 'white'}),
html.P('${0:,.2f}'.format(current_year),
style={'textAlign': 'center',
'color': '#19AAE1',
'fontSize': 15,
'margin-top': '-10px'})
]
@app.callback(Output('text2', 'children'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years):
sales10 = sales.groupby(['Year'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales10['PY'] = sales10['Sales'].shift(1)
previous_year = sales10[(sales10['Year'] == select_years)]['PY'].sum()
return [
html.H6(children='Previous Year',
style={'textAlign': 'center',
'color': 'white'}),
html.P('${0:,.2f}'.format(previous_year),
style={'textAlign': 'center',
'color': '#19AAE1',
'fontSize': 15,
'margin-top': '-10px'})
]
@app.callback(Output('text3', 'children'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years):
sales11 = sales.groupby(['Year'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales11['YOY Growth'] = sales11['Sales'].pct_change()
sales11['YOY Growth'] = sales11['YOY Growth'] * 100
growth_year = sales11[(sales11['Year'] == select_years)]['YOY Growth'].sum()
return [
html.H6(children='YOY Growth',
style={'textAlign': 'center',
'color': 'white'}),
html.P('{0:,.2f}%'.format(growth_year),
style={'textAlign': 'center',
'color': '#19AAE1',
'fontSize': 15,
'margin-top': '-10px'})
]
...
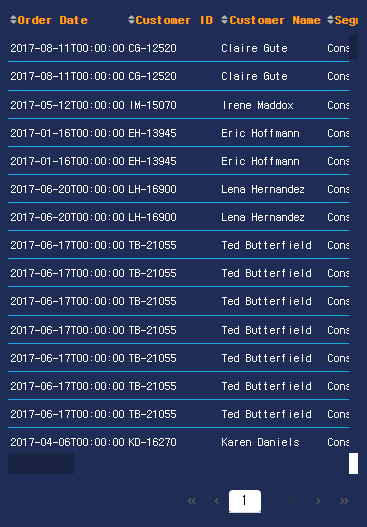
(8) 테이블 추가
- 이번에는 그래프가 아닌 Table을 추가하는 코드를 작성한다.
- Div 태그 안에, 텍스트가 업데이트 될 Div가 추가가 된 것을 기억한다.
- 이번에는 Div 태그를 분리해야 한다. 1행, 2행으로 분리해야 한다.
- Dash 테이블을 참조한다.
import dash_table as dt
...
# (7) 연도별 주요 지표
html.Div([
html.Div(id='text1'),
html.Div(id='text2'),
html.Div(id='text3'),
], className='create_container2 two columns'), # 연도별 주요 지표
], className='row flex-display'), # 상위 Div
# 하위 Div
html.Div([
# (8) 테이블 생성
html.Div([
dt.DataTable(id='my_datatable',
columns=[{'name': i, 'id': i} for i in
sales.loc[:, ['Order Date', 'Customer ID', 'Customer Name',
'Segment', 'City', 'State', 'Region',
'Category', 'Sub-Category', 'Product Name',
'Sales', 'Year', 'Month']]],
virtualization=True,
style_cell={'textAlign': 'left',
'min-width': '100px',
'backgroundColor': '#1f2c56',
'color': '#FEFEFE',
'border-bottom': '0.01rem solid #19AAE1'},
style_header={'backgroundColor': '#1f2c56',
'fontWeight': 'bold',
'font': 'Lato, sans-serif',
'color': 'orange',
'border': '#1f2c56'},
style_as_list_view=True,
style_data={'styleOverflow': 'hidden', 'color': 'white'},
fixed_rows={'headers': True},
sort_action='native',
sort_mode='multi')
], className='create_container2 three columns'), # 테이블 생성
...
], id="mainContainer", style={'display': "flex", "flex-direction": "column"}) # app.layout = html.Div
- 이번에는 Callback을 작성한다.
# (8) 테이블 생성
@app.callback(Output('my_datatable', 'data'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years, radio_items):
data_table = sales[(sales['Year'] == select_years) & (sales['Segment'] == radio_items)]
return data_table.to_dict('records')
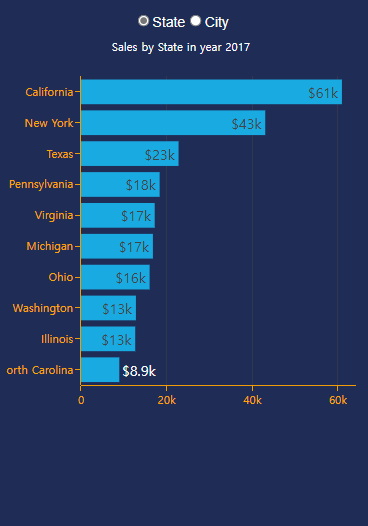
(9) 가로형 막대 그래프
- 이번에는 State, City와 관련된 막대 그래프를 작성한다. 먼저 골격을 우선 작성한다.
], className='create_container2 three columns'), # 테이블 생성
# (9) 가로형 막대 그래프 (State, City)
html.Div([
dcc.RadioItems(id='radio_items2',
labelStyle={'display': 'inline-block'},
value='State',
options=[{'label': 'State', 'value': 'State'},
{'label': 'City', 'value': 'City'}],
style={'text-align': 'center', 'color': 'white'},
className='dcc_compon'),
dcc.Graph(id='bar_chart_2', config={'displayModeBar': 'hover'}, ),
], className='create_container2 three columns'), # 가로형 막대 그래프
- 이번에는 Callback 함수를 작성한다.
...
# (9) 막대형 차트
@app.callback(Output('bar_chart_2', 'figure'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items2', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years, radio_items, radio_items2):
sales12 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'State', 'Segment'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales13 = sales12[(sales12['Year'] == select_years) & (sales12['Segment'] == radio_items)].sort_values(by=['Sales'],
ascending=False).nlargest(
10, columns=['Sales'])
sales14 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'City', 'Segment'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales15 = sales14[(sales14['Year'] == select_years) & (sales14['Segment'] == radio_items)].sort_values(by=['Sales'],
ascending=False).nlargest(
10, columns=['Sales'])
if radio_items2 == 'State':
return {
'data': [
go.Bar(
x=sales13['Sales'],
y=sales13['State'],
text=sales13['Sales'],
texttemplate='$' + '%{text:,.2s}',
textposition='auto',
orientation='h',
marker=dict(color='#19AAE1'),
hoverinfo='text',
hovertext=
'<b>Year</b>: ' + sales13['Year'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Segment</b>: ' + sales13['Segment'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>State</b>: ' + sales13['State'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sales</b>: $' + [f'{x:,.0f}' for x in sales13['Sales']] + '<br>'
),
],
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales by State in year' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.99,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 12},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=15),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#010915',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7},
margin=dict(t=40, r=0),
xaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)),
yaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
autorange='reversed',
showline=False,
showgrid=False,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)
)
)
}
elif radio_items2 == 'City':
return {
'data': [
go.Bar(
x=sales15['Sales'],
y=sales15['City'],
text=sales15['Sales'],
texttemplate='$' + '%{text:,.2s}',
textposition='auto',
orientation='h',
marker=dict(color='#19AAE1'),
hoverinfo='text',
hovertext=
'<b>Year</b>: ' + sales15['Year'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Segment</b>: ' + sales15['Segment'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>City</b>: ' + sales15['City'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sales</b>: $' + [f'{x:,.0f}' for x in sales15['Sales']] + '<br>'
),
],
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales by City in year' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.99,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 12},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=15),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#010915',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7},
margin=dict(t=40, r=0),
xaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=True,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)),
yaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
autorange='reversed',
showline=False,
showgrid=False,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)
)
)
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run_server(debug=True)
(10) 버블 차트 (Bubble Chart)
- Sales에 대한 각 월별 버블 차트를 작성해본다.
...
], className='create_container2 three columns'), # 가로형 막대 그래프
# (10) 산점도 그래프
html.Div([
dcc.Graph(id='bubble_chart', config={'displayModeBar': 'hover'}, )
], className='create_container2 six columns', style={'width': '930px'})
], className='row flex-display') # 산점도 그래프
], id="mainContainer", style={'display': "flex", "flex-direction": "column"}) # app.layout = html.Div
- 이번에는 Callback 함수를 작성한다.
...
# (10) 산점도 그래프
@app.callback(Output('bubble_chart', 'figure'),
[Input('select_years', 'value')],
[Input('radio_items', 'value')])
def update_graph(select_years, radio_items):
sales16 = sales.groupby(['Year', 'Month', 'Segment', 'State', 'City'])['Sales'].sum().reset_index()
sales18 = sales16[(sales16['Year'] == select_years) & (sales16['Segment'] == radio_items)]
return {
'data': [
go.Scatter(
x=sales18['Month'],
y=sales18['Sales'],
mode='markers',
line=dict(width=3, color='orange'),
marker=dict(color=sales18['Sales'],
colorscale='HSV',
showscale=False,
size=sales18['Sales'] / 250,
symbol='circle',
line=dict(color='MediumPurple', width=2)),
hoverinfo='text',
hovertext=
'<b>Year</b>: ' + sales18['Year'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Month</b>: ' + sales18['Month'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Segment</b>: ' + sales18['Segment'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>State</b>: ' + sales18['State'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>City</b>: ' + sales18['City'].astype(str) + '<br>' +
'<b>Sales</b>: $' + [f'{x:,.0f}' for x in sales18['Sales']] + '<br>'
),
],
'layout': go.Layout(
title={'text': 'Sales by state and city in Year' + ' ' + str((select_years)),
'y': 0.99,
'x': 0.5,
'xanchor': 'center',
'yanchor': 'top'},
titlefont={'color': 'white',
'size': 12},
font=dict(family='sans-serif',
color='white',
size=12),
hovermode='closest',
paper_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
plot_bgcolor='#1f2c56',
legend={'orientation': 'h',
'bgcolor': '#010915',
'xanchor': 'center', 'x': 0.5, 'y': -0.7},
margin=dict(t=40, l=0, r=0),
xaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=True,
showgrid=False,
showticklabels=True,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)),
yaxis=dict(title='<b></b>',
color='orange',
showline=False,
showgrid=True,
showticklabels=False,
linecolor='orange',
linewidth=1,
ticks='outside',
tickfont=dict(
family='Aerial',
color='orange',
size=12
)
)
)
}
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run_server(debug=True)
References
-
Dash app layout and css file
-
dash html components
-
dash html components
-
dash basic callbacks
-
Indicator
-
pie chart
-
line chart
-
bar chart
-
Range slider
-
data table
-
marker style
-
bubble chart
