Geospatial Analysis Using Python - Basic
Page content
강의 홍보
- 취준생을 위한 강의를 제작하였습니다.
- 본 블로그를 통해서 강의를 수강하신 분은 게시글 제목과 링크를 수강하여 인프런 메시지를 통해 보내주시기를 바랍니다.
스타벅스 아이스 아메리카노를 선물로 보내드리겠습니다.
- [비전공자 대환영] 제로베이스도 쉽게 입문하는 파이썬 데이터 분석 - 캐글입문기
개요
- 파이썬을 활용한 공간 시각화에 대해 기술하도록 한다.
- 각 패키지의 쓰임새와 용도를 확인하도록 한다.
- 예제를 통해 확인한 뒤, 국내 데이터를 적용해보도록 한다.
- 한글 폰트상의 문제점 외에 다른 문제점은 없는지 확인해본다.
- 우선 참고한 자료는 아래와 같다.
기본 환경설정
- 구글 코랩의 환경설정을 살펴보자.
- 파이썬 버전 3.6.9을 현재 사용중이다. (2020년 8월 기준)
import sys
sys.version_info
sys.version_info(major=3, minor=6, micro=9, releaselevel='final', serial=0)
- 이번에는
OS플랫폼을 확인한다.- 현재
Ubuntu 18.04버전을 사용중이다.
- 현재
import platform
platform.platform()
'Linux-4.19.112+-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-18.04-bionic'
- 이번에는 CPU 관련된 정보를 확인해본다.
- CPU 제논 2.3GHz
!cat /proc/cpuinfo
processor : 0
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 79
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU @ 2.20GHz
stepping : 0
microcode : 0x1
cpu MHz : 2200.000
cache size : 56320 KB
physical id : 0
siblings : 2
core id : 0
cpu cores : 1
apicid : 0
initial apicid : 0
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc cpuid tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single ssbd ibrs ibpb stibp fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm rdseed adx smap xsaveopt arat md_clear arch_capabilities
bugs : cpu_meltdown spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass l1tf mds swapgs taa
bogomips : 4400.00
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 46 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
processor : 1
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 79
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU @ 2.20GHz
stepping : 0
microcode : 0x1
cpu MHz : 2200.000
cache size : 56320 KB
physical id : 0
siblings : 2
core id : 0
cpu cores : 1
apicid : 1
initial apicid : 1
fpu : yes
fpu_exception : yes
cpuid level : 13
wp : yes
flags : fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc rep_good nopl xtopology nonstop_tsc cpuid tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single ssbd ibrs ibpb stibp fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 hle avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rtm rdseed adx smap xsaveopt arat md_clear arch_capabilities
bugs : cpu_meltdown spectre_v1 spectre_v2 spec_store_bypass l1tf mds swapgs taa
bogomips : 4400.00
clflush size : 64
cache_alignment : 64
address sizes : 46 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
power management:
- 메모리 정보를 확인해본다.
- 무료 버전의 경우 약
13GB를 사용할 수 있다.
- 무료 버전의 경우 약
!cat /proc/meminfo
MemTotal: 13333552 kB
MemFree: 10691516 kB
MemAvailable: 12499620 kB
Buffers: 76712 kB
Cached: 1886808 kB
SwapCached: 0 kB
Active: 668976 kB
Inactive: 1678968 kB
Active(anon): 360932 kB
Inactive(anon): 360 kB
Active(file): 308044 kB
Inactive(file): 1678608 kB
Unevictable: 0 kB
Mlocked: 0 kB
SwapTotal: 0 kB
SwapFree: 0 kB
Dirty: 1992 kB
Writeback: 0 kB
AnonPages: 384360 kB
Mapped: 179824 kB
Shmem: 972 kB
Slab: 164416 kB
SReclaimable: 124572 kB
SUnreclaim: 39844 kB
KernelStack: 3872 kB
PageTables: 4924 kB
NFS_Unstable: 0 kB
Bounce: 0 kB
WritebackTmp: 0 kB
CommitLimit: 6666776 kB
Committed_AS: 2491516 kB
VmallocTotal: 34359738367 kB
VmallocUsed: 0 kB
VmallocChunk: 0 kB
Percpu: 952 kB
AnonHugePages: 0 kB
ShmemHugePages: 0 kB
ShmemPmdMapped: 0 kB
HugePages_Total: 0
HugePages_Free: 0
HugePages_Rsvd: 0
HugePages_Surp: 0
Hugepagesize: 2048 kB
Hugetlb: 0 kB
DirectMap4k: 107708 kB
DirectMap2M: 5134336 kB
DirectMap1G: 10485760 kB
- GPU 사용이 가능하면
/device:GPU:0이라고 확인이 될 것이다.- 만약 런타임 유형 변경에서
None으로 설정 하면,' '만 출력이 된다.
- 만약 런타임 유형 변경에서
import tensorflow as tf
tf.test.gpu_device_name()
'/device:GPU:0'
한글 폰트 설정
- 시각화 출력 시, 한글 폰트는 별도로 설치 및 설정해줘야 한다.
- 폰트 설치, 폰트 불러오기, 그리고 런타임 재실행 순으로 해준다.
(1) 폰트 설치
- 우분투 명령어
apt-get을 통해나눔폰트를 설치한다.
!apt-get update -qq
!apt-get install fonts-nanum* -qq
Selecting previously unselected package fonts-nanum.
(Reading database ... 144540 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../fonts-nanum_20170925-1_all.deb ...
Unpacking fonts-nanum (20170925-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package fonts-nanum-eco.
Preparing to unpack .../fonts-nanum-eco_1.000-6_all.deb ...
Unpacking fonts-nanum-eco (1.000-6) ...
Selecting previously unselected package fonts-nanum-extra.
Preparing to unpack .../fonts-nanum-extra_20170925-1_all.deb ...
Unpacking fonts-nanum-extra (20170925-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package fonts-nanum-coding.
Preparing to unpack .../fonts-nanum-coding_2.5-1_all.deb ...
Unpacking fonts-nanum-coding (2.5-1) ...
Setting up fonts-nanum-extra (20170925-1) ...
Setting up fonts-nanum (20170925-1) ...
Setting up fonts-nanum-coding (2.5-1) ...
Setting up fonts-nanum-eco (1.000-6) ...
Processing triggers for fontconfig (2.12.6-0ubuntu2) ...
(2) 폰트 설정
# 설치된 나눔 폰트 출력
# 만약, 설치했는데도, 리스트가 [] 로 출력된다면 런타임을 다시 시작해주세요
import matplotlib.font_manager as fm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys_font=fm.findSystemFonts()
nanum_font = [f for f in sys_font if 'Nanum' in f]
print(f"nanum_font number: {len(nanum_font)}")
nanum_font
!python --version
def current_font():
print(f"현재 설정된 폰트 글꼴: {plt.rcParams['font.family']}, 현재 설정된 폰트 사이즈: {plt.rcParams['font.size']}") # 파이썬 3.6 이상 사용가능
current_font()
nanum_font number: 31
Python 3.6.9
현재 설정된 폰트 글꼴: ['sans-serif'], 현재 설정된 폰트 사이즈: 10.0
- 현재 설정된 폰트 글꼴은
['sans-serif']인 것으로 확인된다.- 이제
sans-serif를 나눔고딕으로 변경한다.
- 이제
path = '/usr/share/fonts/truetype/nanum/NanumBarunGothic.ttf'
font_name = fm.FontProperties(fname=path, size=14).get_name()
plt.rc('font', family=font_name)
current_font()
현재 설정된 폰트 글꼴: ['NanumBarunGothic'], 현재 설정된 폰트 사이즈: 10.0
(3) 전체 노트북에 반영
- 이렇게 설정이 된 후에는
fm._rebuild()를 통해 재 설정 한다. - 현재 나올 모든 환경 설정을 아래와 같이 설정한다.
fm._rebuild()
# 노트북 전체 폰트 및 차트 크기 설정
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = 'NanumBarunGothic'
plt.rcParams["font.size"] = 14
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (12,6)
# matplotlib에서 마이너스 부호가 깨질 때
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
print('설정 되어있는 폰트 사이즈 : {}'.format(plt.rcParams['font.size']))
print('설정 되어있는 폰트 글꼴 : {}'.format(plt.rcParams['font.family']))
print('설정 되어있는 차트 크기 : {}'.format(plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]))
설정 되어있는 폰트 사이즈 : 14.0
설정 되어있는 폰트 글꼴 : ['NanumBarunGothic']
설정 되어있는 차트 크기 : [12.0, 6.0]
(4) 공간시각화 관련 패키지 설정 방법
- rtree 패키지 설치가 문제가 될 수 있기 때문에 다음과 같이 설치를 진행한다.
!apt install libspatialindex-dev
!pip install rtree
!pip install geopandas
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree
Reading state information... Done
libspatialindex-dev is already the newest version (1.8.5-5).
The following package was automatically installed and is no longer required:
libnvidia-common-440
Use 'apt autoremove' to remove it.
0 upgraded, 0 newly installed, 0 to remove and 60 not upgraded.
Requirement already satisfied: rtree in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (0.9.4)
Requirement already satisfied: setuptools in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from rtree) (49.2.0)
Requirement already satisfied: geopandas in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (0.8.1)
Requirement already satisfied: pyproj>=2.2.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from geopandas) (2.6.1.post1)
Requirement already satisfied: fiona in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from geopandas) (1.8.13.post1)
Requirement already satisfied: shapely in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from geopandas) (1.7.0)
Requirement already satisfied: pandas>=0.23.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from geopandas) (1.0.5)
Requirement already satisfied: cligj>=0.5 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fiona->geopandas) (0.5.0)
Requirement already satisfied: attrs>=17 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fiona->geopandas) (19.3.0)
Requirement already satisfied: six>=1.7 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fiona->geopandas) (1.15.0)
Requirement already satisfied: munch in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fiona->geopandas) (2.5.0)
Requirement already satisfied: click<8,>=4.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fiona->geopandas) (7.1.2)
Requirement already satisfied: click-plugins>=1.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from fiona->geopandas) (1.1.1)
Requirement already satisfied: python-dateutil>=2.6.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas>=0.23.0->geopandas) (2.8.1)
Requirement already satisfied: numpy>=1.13.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas>=0.23.0->geopandas) (1.18.5)
Requirement already satisfied: pytz>=2017.2 in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (from pandas>=0.23.0->geopandas) (2018.9)
구글 드라이브와 연동
- 우선 구글 드라이브와 계정 연동을 진행한다.
# Mount Google Drive
from google.colab import drive # import drive from google colab
ROOT = "/content/drive" # default location for the drive
print(ROOT) # print content of ROOT (Optional)
drive.mount(ROOT) # we mount the google drive at /content/drive
/content/drive
Drive already mounted at /content/drive; to attempt to forcibly remount, call drive.mount("/content/drive", force_remount=True).
- 데이터가 있는 경로로 이동한다.
from os.path import join
MY_GOOGLE_DRIVE_PATH = 'My Drive/Colab Notebooks/inflearn/Python/Kaggle_Edu/02_kaggle_eda/03_map/data' # 프로젝트 경로
PROJECT_PATH = join(ROOT, MY_GOOGLE_DRIVE_PATH) # 프로젝트 경로
print(PROJECT_PATH)
/content/drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/inflearn/Python/Kaggle_Edu/02_kaggle_eda/03_map/data
%cd "{PROJECT_PATH}"
/content/drive/My Drive/Colab Notebooks/inflearn/Python/Kaggle_Edu/02_kaggle_eda/03_map/data
%ls
[0m[01;34m'상가(상권)정보_201912.'[0m/ customer_rate_02.xlsx pivot_table_04.xlsx
census.csv merge_03.xlsx
city.geojson missing_values_01.xlsx
공간시각화 파일에 대한 기본 개념
geometry는Point,Line,Polygon을 저장할 수 있다.- 파일의 구성도는 다음과 같다.
$ ls map_files/
map.dbf
map.shp
map.shx
shp는 전체geometry를 의미한다.dbf는 각geometry에 대한 속성(atrributes)값을 가지고 있다.shx는 각 속성 값을shp안에 있는geometry를 연결한다.
Geopandas 의존성
GeoJSON은 MultiPoint, MultiLineString, MultiPolygon을 포함한 MultiGeometry를 지원함.geojson을geopandas로 읽게 될 경우,properties는GeoDataFrame이 된다.
(1) Geopandas의 개념
geopandas는 크게 2가지의 데이터 의존성이 있다.Vector: points, lines, and polygons.RASTER: 일종의 격자(grid)로 생각하면 된다. (예: Topographical Map)
- 크게 2개의 Library가 필요하다.
Fiona:Open GIS Simple Features와 파이썬과geopandas를 연결하는 일종의 다리 역할을 수행한다.GDAL은rater데이터를 변환하는 것OGR은 vector 데이터를 변환하는 것

Coordinate System
- Coordinate 시스템은 크게 2가지로 구분된다.
- EPSG: 4326
- 구글 Earth가 사용하는 시스템이며,
decimal degree를 사용한다.
- 구글 Earth가 사용하는 시스템이며,
- EPSG: 3857
- Google Maps, Bing Maps, Open Street Maps 등이 사용하는 시스템이며,
meter를 거리계로 사용한다.
- Google Maps, Bing Maps, Open Street Maps 등이 사용하는 시스템이며,
- EPSG: 4326
(1) shapely package
geometry는 geoDataFrame의 필수적인 요소이다.- 판다스 데이터프레임에 존재하는
위도&경도를 geoDataFramegeometry로 변환할 때 사용된다.
예제 실습 구현
- 이제 간단하게
geojson데이터를 활용해서 구현해본다.
(1) 예제 데이터 수집 및 변환
geojson데이터를 가져와서 확인해본다.
import geopandas as gpd
url = "https://assets.datacamp.com/production/repositories/2409/datasets/9ea668811fb71fa77ad29362ea5299f05ad150af/school_districts.geojson"
school_districts = gpd.read_file(url)
school_districts.head(1)
| first_name | city | zip | state | last_name | address | position | term_expir | district | phone | geometry | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Dr. Sharon | Nashville | 37218 | gentryfordistrict1@comcast.net | TN | Gentry | 6108 Beals Lane | Member | 2016 | 1 | 615-268-5269 | MULTIPOLYGON (((-86.77136 36.38357, -86.77134 ... |
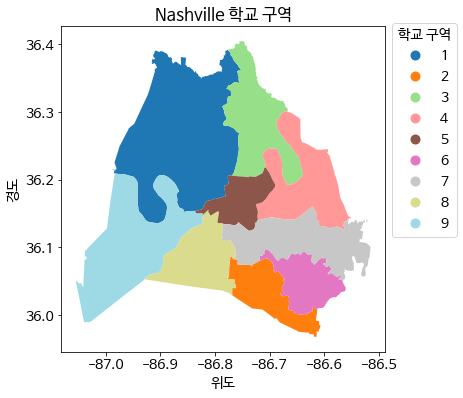
(2) 예제 데이터 시각화
plot()함수를 활용하여 시각화를 그려본다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 범례
legend_styles = {'title': '학교 구역',
'loc': 'upper left', 'bbox_to_anchor': (1, 1.03), 'ncol': 1}
school_districts.plot(column = 'district', cmap = 'tab20', legend = True, legend_kwds = legend_styles)
plt.xlabel('위도')
plt.ylabel('경도')
plt.title('Nashville 학교 구역')
plt.show();
- 이번에는
tab20을summer로 바꿔본다.
school_districts.plot(column = 'district', cmap = 'summer', legend = True, legend_kwds = legend_styles)
plt.xlabel('위도')
plt.ylabel('경도')
plt.title('Nashville 학교 구역')
plt.show();
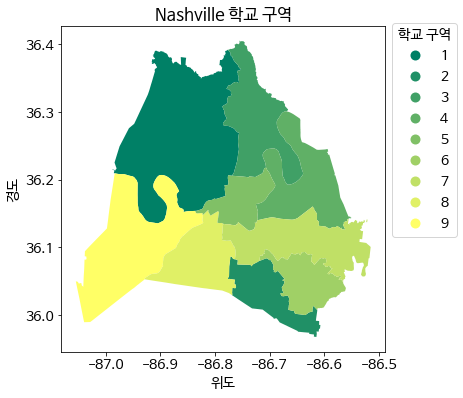
cmap에 인수값을 변환하여 적용할 수 있다.
(3) Coordinate 시스템 변환
- 현재
school_districs는epsg:4326시스템에 의해 운용되고 있다. 이를 구글 맵과 같은 것으로 바꿔준다.
print(school_districts.head(1))
print(school_districts.crs)
first_name ... geometry
0 Dr. Sharon ... MULTIPOLYGON (((-86.77136 36.38357, -86.77134 ...
[1 rows x 12 columns]
epsg:4326
school_districts.geometry = school_districts.geometry.to_crs(epsg = 3857)
print(school_districts.head(1))
print(school_districts.crs)
first_name ... geometry
0 Dr. Sharon ... MULTIPOLYGON (((-9659344.056 4353528.767, -965...
[1 rows x 12 columns]
epsg:3857
-
geometry의 값이 변환된 것을 알 수 있다. -
이번에는
Nashville NeighborhoodsGIS 데이터를 변환하도록 한다.
import geopandas as gpd
url = 'https://assets.datacamp.com/production/repositories/2409/datasets/a534dea1e6a99373a5a8e9c2060ad8fb6b74e13c/neighborhoods.geojson'
neighborhoods = gpd.read_file(url)
neighborhoods.geometry = neighborhoods.geometry.to_crs(epsg = 3857)
print(neighborhoods.head(1))
print(neighborhoods.crs)
name geometry
0 Historic Buena Vista MULTIPOLYGON (((-9661987.512 4324832.657, -966...
epsg:3857
(4) 데이터 변환
shapely패키지를 활용해서pandas DataFrame에서GeoDataFrame으로 변환한다.
import pandas as pd
url = 'https://assets.datacamp.com/production/repositories/2409/datasets/284dd5ef16418d161af519d30ecc8471a23210ea/public_art.csv'
art = pd.read_csv(url)
art.drop('Mapped Location', axis=1, inplace=True)
print(art.info())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 132 entries, 0 to 131
Data columns (total 9 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Title 132 non-null object
1 Last Name 132 non-null object
2 First Name 122 non-null object
3 Location 131 non-null object
4 Medium 128 non-null object
5 Type 132 non-null object
6 Description 87 non-null object
7 Latitude 132 non-null float64
8 Longitude 132 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(7)
memory usage: 9.4+ KB
None
art데이터에, art[‘geometry’]를 추가하도록 해본다.
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
from shapely.geometry import Point
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Print the first few rows of the art DataFrame
print(art.head())
# Create a geometry column from lng & lat
art['geometry'] = art.apply(lambda x: Point(float(x.Longitude), float(x.Latitude)), axis=1)
# Create a GeoDataFrame from art and verify the type
art_geo = gpd.GeoDataFrame(art, crs = neighborhoods.crs, geometry = art.geometry)
print(type(art_geo))
Title ... Longitude
0 [Cross Country Runners] ... -86.83660
1 [Fourth and Commerce Sculpture] ... -86.77774
2 12th & Porter Mural ... -86.78817
3 A Splash of Color ... -86.79975
4 A Story of Nashville ... -86.78205
[5 rows x 9 columns]
<class 'geopandas.geodataframe.GeoDataFrame'>
(5) 공간 데이터 조인
- 공간데이터를 방법은
sjoin()함수를 사용한다.- 함수에 대한 구체적인 사용 예제는 sjoin()을 활용한다.
- 이 때,
intersects,within,contains의 차이점에 대해 이해한다.
import geopandas as gpd
url = 'https://assets.datacamp.com/production/repositories/2409/datasets/a534dea1e6a99373a5a8e9c2060ad8fb6b74e13c/neighborhoods.geojson'
neighborhoods = gpd.read_file(url)
art_intersects_neighborhoods = gpd.sjoin(art_geo, neighborhoods, op = 'intersects')
print(art_intersects_neighborhoods.shape)
(40, 12)
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:1: UserWarning: CRS mismatch between the CRS of left geometries and the CRS of right geometries.
Use `to_crs()` to reproject one of the input geometries to match the CRS of the other.
Left CRS: EPSG:3857
Right CRS: EPSG:4326
"""Entry point for launching an IPython kernel.
art_within_neighborhoods = gpd.sjoin(art_geo, neighborhoods, op = 'within')
print(art_within_neighborhoods.shape)
(40, 12)
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:1: UserWarning: CRS mismatch between the CRS of left geometries and the CRS of right geometries.
Use `to_crs()` to reproject one of the input geometries to match the CRS of the other.
Left CRS: EPSG:3857
Right CRS: EPSG:4326
"""Entry point for launching an IPython kernel.
art_contains_neighborhoods = gpd.sjoin(art_geo, neighborhoods, op = 'contains')
print(art_contains_neighborhoods.shape)
(0, 12)
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/ipykernel_launcher.py:1: UserWarning: CRS mismatch between the CRS of left geometries and the CRS of right geometries.
Use `to_crs()` to reproject one of the input geometries to match the CRS of the other.
Left CRS: EPSG:3857
Right CRS: EPSG:4326
"""Entry point for launching an IPython kernel.
- 위 객체 중에서는
art_within_neighborhoods을 사용하도록 해본다.
(6) 집계함수
- 이제 각
column에 따라 집계를 하도록 해본다.
neighborhood_art_grouped = art_within_neighborhoods[['name', 'Title']].groupby('name')
print(neighborhood_art_grouped.agg('count').sort_values(by = 'Title', ascending = False))
Title
name
Urban Residents 22
Lockeland Springs 3
Edgehill (ONE) 2
Germantown 2
Hillsboro-West End 2
Inglewood 2
Sunnyside 2
Chestnut Hill (TAG) 1
Historic Edgefield 1
McFerrin Park 1
Renraw 1
Wedgewood Houston (SNAP) 1
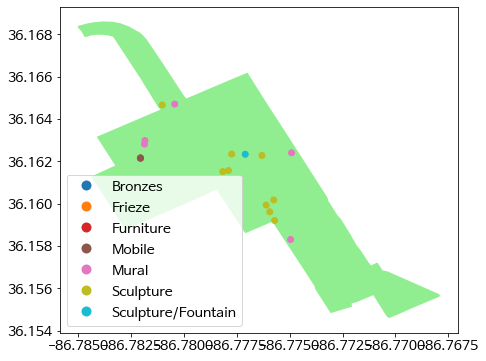
(6) 공간 시각화 구현
- 이렇게 집계된 데이터를 기준으로 공간 시각화를 구현한다.
urban_art = art_within_neighborhoods.loc[art_within_neighborhoods.name == "Urban Residents"]
urban_polygon = neighborhoods.loc[neighborhoods.name == "Urban Residents"]
ax = urban_polygon.plot(color = 'lightgreen')
urban_art.plot(ax = ax, column = 'Type', legend = True);
plt.show()
고양시 데이터 시각화 구현
- 이제 고양시 데이터를 수집해서 시각화를 그려보도록 한다.
(1) 고양시 데이터 수집 및 변환
- 이번에는 고양시의
geojson데이터를 수집 및 변환해본다.
koyang_districts = gpd.read_file('city.geojson')
koyang_districts.head(1)
| EMD_CD | EMD_KOR_NM | geometry | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 41281101 | 주교동 | MULTIPOLYGON (((126.81068 37.65820, 126.81069 ... |
(2) 시각화를 구현
- 주어진 데이터를 토대로 시각화를 구현한다.
koyang_districts.plot(cmap = 'tab20')
plt.xlabel('위도')
plt.ylabel('경도')
plt.title('고양시의 구역')
plt.show();
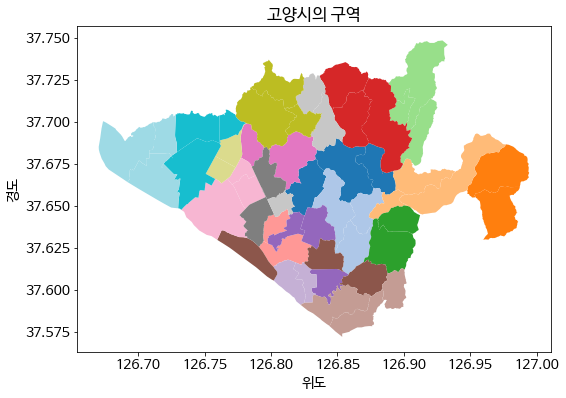
- 고양시의 지도가 그려진 것을 확인할 수 있다.
cmap에 어떤 인수가 들어가는지 확인하기 위해서는 공식 메뉴얼을 참조해본다.
One can also modify the colors used by plot with the cmap option (for a full list of colormaps, see the matplotlib website:
cmap의 시각화 색상을 선택하려면matplotlib에 들어가서 확인해야 한다.
(3) Coordinate 시스템 변환
- 현재
koyang_districts는epsg:4326시스템에 의해 운용되고 있다. 이를 구글 맵과 같은 것으로 바꿔준다.
print(koyang_districts.head(1))
print(koyang_districts.crs)
EMD_CD EMD_KOR_NM geometry
0 41281101 주교동 MULTIPOLYGON (((126.81068 37.65820, 126.81069 ...
epsg:4326
koyang_districts.geometry = school_districts.geometry.to_crs(epsg = 3857)
print(koyang_districts.head(1))
print(koyang_districts.crs)
EMD_CD EMD_KOR_NM geometry
0 41281101 주교동 MULTIPOLYGON (((-9659344.056 4353528.767, -965...
epsg:3857
4326에서3857로 바꿔준 것을 확인할 수 있다.
(4) 인구 데이터 불러오기
- 이제 고양시의 인구 데이터를 불러온다.
census = pd.read_csv('census.csv')
print(census.info())
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 1584 entries, 0 to 1583
Data columns (total 8 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 행정구역 1584 non-null object
1 조회기준 1584 non-null object
2 총인구수 1584 non-null object
3 세대수 1584 non-null object
4 세대당 인구 1584 non-null float64
5 남자 인구수 1584 non-null object
6 여자 인구수 1584 non-null object
7 남여 비율 1584 non-null float64
dtypes: float64(2), object(6)
memory usage: 99.1+ KB
None
- 현재 위 데이터를 보면 위도와 경도가 없다.
- 따라서, 각 행정구역마다 위도 경도가 들어간 합체 데이터가 필요하다.
- 어떻게 해야 할까?
- 이 부분 해결방법에 대한 고민이 필요한 시기이다.
